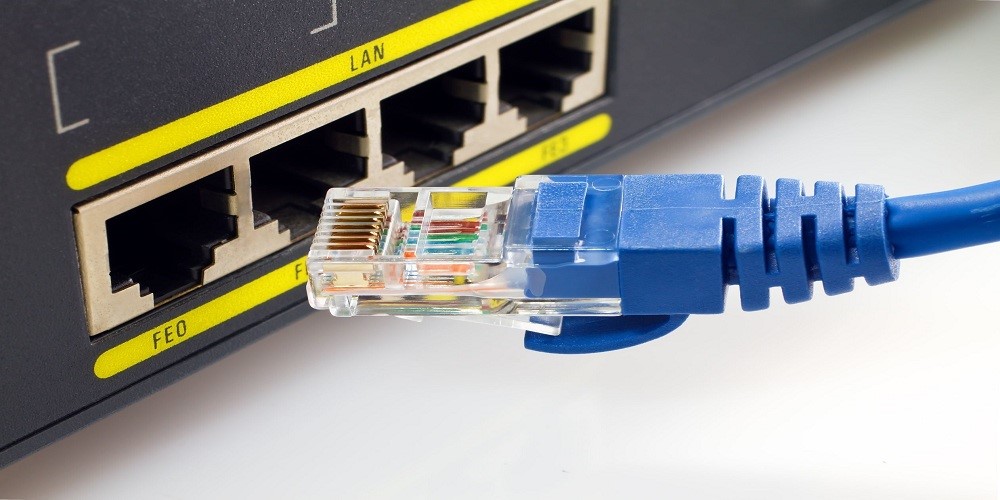
Classic Features of Ethernet Cables
Ethernet cables use a standard protocol for computer connections in the MAN to support the internet. It is a twisted pair cable where some types are shielded while the others are unshielded. These cables are continuously evolving toward better performance and larger area coverage.
Ethernet Cable basics
For connectivity, Ethernet cables depend on the twisted wire pair format. In which two cables are twisted together allows the balance of current. In both wires, current flows in opposite directions making the overall field neutral.
By this method, data can be transferred over substantial lengths without the requirement for excessive precautions.
Key Features
While discussing the Ethernet cables, there are some key features that we need to focus such as:
**· **Speed (Data Rate)
Speed is the amount of data that transmit per second. The data rate of Ethernet cable types carries from 10Mbps to 25Gbps. The speed requirement is directly related to the wire application and network system.
**· **Shielding
To protect cable conductors from EMI, many Ethernet cables are shielded with additional layers. EMI can cause in larger systems because of fluorescent lighting or other reasons. Shielding also prevents the interaction of parallel conductors in cable jackets.
· Cable Length ****
Ethernet cable’s maximum length is up to 100 meters. It is the maximum length at which the cable can transfer data without interference. New Ethernet cables are being introduced with better performance and increased cable length.
**· **Connector Type
Commonly connectors come in various types like BNC, DB, RJ, and USB. Mostly Ethernet cables use RJ45 8-pin connector on both ends for data transmission. These are modular connectors with serial and telecommunication applications.
Categories for Ethernet cables
Based on features and applications, Ethernet cables are divided into eight categories from Cat -1 to Cat-8. Let’s have a brief review of all.
Cat-1
Not recognized by the TIA/EIA standards. Use in ISDN and POTS wiring.
Cat-2 & 4
Not identified by the TIA/EIA standards. These cables are used on 4Mbit/s & 16Mbps token ring networks.
Cat-3
Recognized by TIA/EIA-568-B standards and used for 16MHz frequency data network employing.
Cat-5
Not recognized by the TIA/EIA standards and widely used for 100 to 1000Base-T networks. The Cat 5 cable outmoded the Cat 3 version and remained as Ethernet cabling standard for many years but not recommended now.
Cat-6
Defined in TIA/EIA-568-B standards, improved than Cat 5 and Cat 5e. Prevent noise interference and crosstalk.
Cat-7
Informal number for ISO/IEC 11801 Class F cabling. It contains four separately shielded pairs covered by one shield. Use in the transmission of up to 600 Mbps frequencies.
Cat-8
Latest version of Ethernet cables provides large data transmission, more expensive than Cat 6 and Cat 7.
Online Source
To buy Ethernet cables online, only visit authentic websites with positive reviews. Whether you are looking for a CAT 6 cable, Cat 5 cable, or Cat 8 for your new projects, www.cakeycn.com has got everything you need. Visit the website and get top-notch cables at reasonable prices.
Conclusion
Ethernet cabling can offer a long-distance approach with high speed to local and complex networking than Wi-Fi. The popularity of these cables is due to their specifications and classic features. Some key features of these cables are described above.